Die Cutting Explained
You may well encounter various products that can be die-cut to a custom shape. But what does that mean? And more importantly, how can it help you create the perfect printed product? Read on to learn all about die cutting…
What is Die Cutting?
In the world of printing, die cutting provides a quick and inexpensive way of cutting lots of printed items into identical shapes.
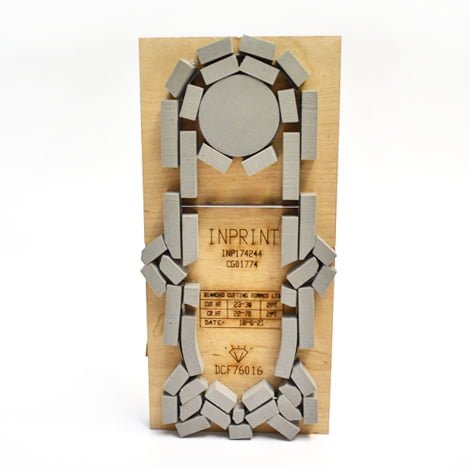
Your design is printed on a square or rectangular sheet of material (typically paper or card), then placed in a machine which has been loaded with a custom-made ‘die’ or ‘punch block’ (a block of wood with a metal blade, bent and folded into the desired shape).
When the machine presses the printed sheet and the die together, it cuts out the shape of the blade into the material in an instant.

Die cutting is for more than just eye catching custom shaped flyers however, it also helps create the more functional aspects of printed products such as pockets and flaps on folders and boxes plus the curves, circles and intricate interlocking elements on our speciality print.


Why is die-cutting beneficial?
Die-cutting allows you to create your desired shape in one fell swoop, without the time consuming need for a digital cutter to wind its way around all the curves and corners. Once you have created your die, you can use it over and over again, allowing you to create hundreds of identical, custom-shaped products.
Which materials can be die-cut?
Due to the nature of the ‘punch-out’ style of cutting, die-cutting works best on low strength materials such as paper and card. Minimum paper weight to die cut is 170gsm (approx 140micron) and the maximum is 500gsm (approx 600micron). Microns is thickness measured as thousandths of a millimetre.
What about foamboard, correx and dibond?
Heavier weight large format materials will have to be digitally die cut. Unlike die cutting which uses physical dies to create the shape, digital cutting uses a blade which follows a computer-programmed path to create the shape.
A digital cutting machine consists of a flat table area and a set of cutting, milling and scoring attachments mounted on an arm. This arm allows the cutter to move left, right, forwards and backwards.
The printed sheet is placed on the table, and the cutter travels across the sheet along the programmed path to cut out the shape.
Digital die cut paper and card
Technology moves fast and now you are able to produce “die free” cutting with excellent results on a whole range of weights of paper and card!
This has the advantage of keeping both cost and production times down, due to bypassing the need for an expensive die block.
While not being able to match the output volume of traditional die cutting the digital die cutting options are perfect for lower runs of print or prototypes for larger die cutting formes.
